Tag: Stanford University
New approaches to high-resolution geological simulations

Geological and reservoir modelling are critical for geological exploration, resource extraction, and geoengineering projects. Current workflows and datasets record geological variations on metre or decimetre scales. However, many relevant geological structures exist at sub-centimetre scales. Dr Achyut Mishra and Professor Ralf Haese at the University of Melbourne, Australia – part of the international research consortium GeoCquest – have developed a […]
Read More… from New approaches to high-resolution geological simulations
How electrons and phonons promote heat transfer in material systems

Miniaturisation is one of the key features of current and future technologies for information processing and control. However, the ability to reduce the size of an electronic component is limited by a decrease in electrical conductivity and an increase in thermal energy dissipation as the device approaches the nano-scale regime. By studying the electronic and vibrational characteristics of high-purity iridium […]
Read More… from How electrons and phonons promote heat transfer in material systems
Advancing imaging biomarker development and translation through the National Cancer Imaging Translational Accelerator (NCITA)
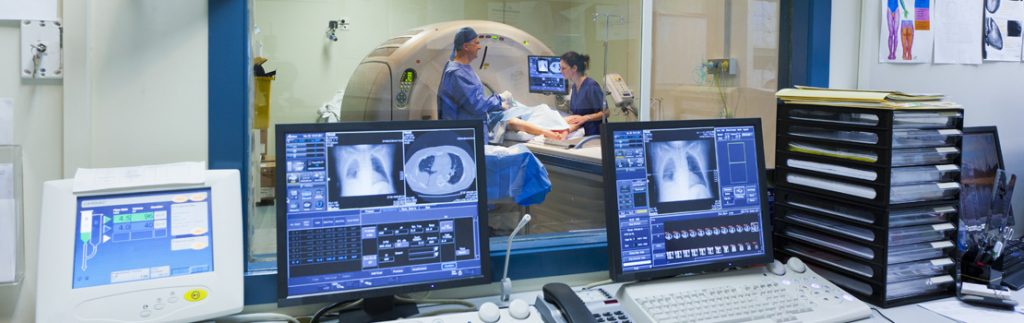
It is estimated that someone is diagnosed with cancer every two minutes in the UK. Clinical imaging offers a minimally invasive way of diagnosing and managing a variety of cancers. The National Cancer Imaging Translational Accelerator (NCITA) consortium now provides researchers with the infrastructure to conduct high-quality, multi-centre clinical research in the quest to develop standardised imaging biomarkers and accelerate […]
Free Electron Lasers: The Biggest and Brightest Light Sources

Creating focused, well-behaved beams of electrons is no easy task, but something that Dr Sergio Carbajo and his team at Stanford University and the SLAC National Accelerator laboratory are experts in. They are developing new technologies to control electron generation for some of the world’s biggest and brightest lasers to make it possible to film exactly what happens in the […]
Read More… from Free Electron Lasers: The Biggest and Brightest Light Sources