Tag: USA
Transdisciplinary philosophy: An interview with Professor Nayef Al-Rodhan

What is Transdisciplinary Philosophy? And what is the paradigm’s intellectual and practical significance for individuals, societal frameworks and the global system? At its most basic level, Transdisciplinary Philosophy is a call for a broader, more inclusive approach to thinking and acting in the world. It is an intellectual approach for addressing complex global challenges by transcending the boundaries of traditional […]
Read More… from Transdisciplinary philosophy: An interview with Professor Nayef Al-Rodhan
Understanding neonatal brain injury proteinopathy: Implications for adult-onset neurodegenerative disease

Neonatal encephalopathy is damage to the brain caused by the disruption of its blood supply before and during childbirth and other reasons such as prematurity and maternal-foetal infection. It can often lead to death. Survivors can have long-term cognitive, emotional, and behavioural effects. Lee J Martin, Professor of Anaesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine and Pathology at Johns Hopkins University, USA, […]
Psychotropic medications for behavioural disorders in children: Are we getting it right?

Psychotropic medications are used to treat mental health conditions by regulating the levels of certain chemicals in the brain. In children, they are often used to treat behavioural issues including attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). As one of many treatment options, psychotropic medicines should not always be the first choice for children, especially since their effects on their developing brain are […]
Glycomimetic peptides as powerful anti-inflammatory treatments
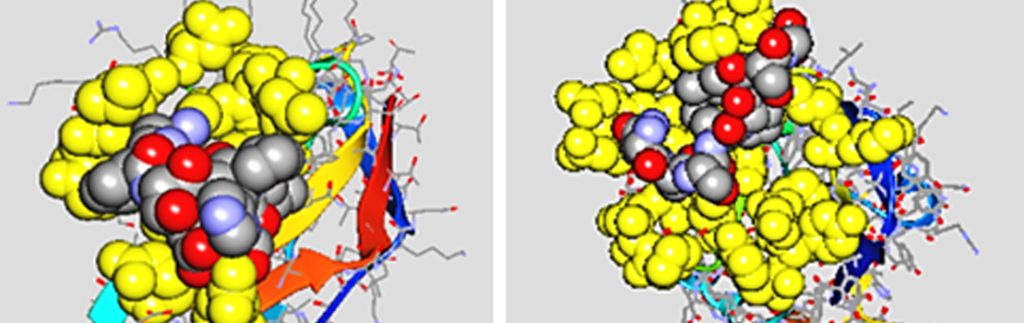
Glycan (sugar)-binding lectin-type receptors on immune cells have the potential to serve as therapeutic targets. However, many of these receptors are not targeted because of a lack of suitable binding agents. Professor J Kenneth Hoober and Dr Laura L Eggink, co-founders of Susavion Biosciences, Inc, and Wild Boar Biosciences, LLC, have created peptide mimetics of glycans that show greater flexibility […]
Read More… from Glycomimetic peptides as powerful anti-inflammatory treatments
Nivolumab against lung cancer: How is the gut–lung axis involved?
The study of the gut microbiome, which is the total of all the microbes living in the intestines, has been shown to not only play an important role in the health of the bowel itself, but also in the health of distant organs such as the lungs. Lung cancer is one of the diseases that is often difficult to treat […]
Read More… from Nivolumab against lung cancer: How is the gut–lung axis involved?
Do joint manipulation sounds make a difference in physical therapy outcomes?
Joint manipulation, a manual technique used to decrease pain and improve joint mobility in physical therapy, is often accompanied by audible pops called joint manipulation sounds. Practitioners and patients tend to believe that feeling or hearing these pops means that their treatment was successful and that their symptoms will improve. Dr Rob Sillevis at Florida Gulf Coast University has evaluated […]
Read More… from Do joint manipulation sounds make a difference in physical therapy outcomes?
Rare disease drug development: Time for a new approach?

A limited patient population is a key challenge in rare disease drug development. Professor Shein-Chung Chow of Duke University School of Medicine, USA and his research partners explore innovative approaches to overcome this challenge. These include using external control, selecting appropriate study endpoints, and justifying sample size based on probability statements. They propose the use of a complex innovative two-stage […]
Read More… from Rare disease drug development: Time for a new approach?
Barth syndrome: A potential treatment for a rare disease
Barth syndrome is a rare disorder in males caused by a variant of the gene TAFAZZIN. It affects the metabolism of the fat molecule cardiolipin in mitochondria, resulting in the dysfunction of skeletal muscle and the heart. The syndrome doesn’t have a specific therapy, so patients who suffer from it have health problems their entire lives and are more likely […]
Read More… from Barth syndrome: A potential treatment for a rare disease
CO2 conversion for a circular carbon economy

A circular carbon economy – where carbon released from the Earth is captured and repurposed – is a promising concept, and CO2 conversion to sustainable products has been at the forefront of research. Dr Gary Grim at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, USA, has been working on quantifying the feasibility of CO2 conversion. He provides a detailed comparison of available […]
Read More… from CO2 conversion for a circular carbon economy
Curing the incurable: RNA isoforms may hold the key to defeating Alzheimer’s disease
Groundbreaking research on RNA isoforms in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has revealed another layer of genetic complexity that has been previously overlooked. Using cutting-edge sequencing technology, Dr. Mark Ebbert and colleagues at the Sanders-Brown Center on Aging at the University of Kentucky, USA, performed a detailed analysis of RNA isoforms in the human brain. They discovered multiple, previously unknown RNA isoforms […]
Read More… from Curing the incurable: RNA isoforms may hold the key to defeating Alzheimer’s disease