Tag: x-rays
X-ray ptychography: Seeing chromosome abnormalities in a new light
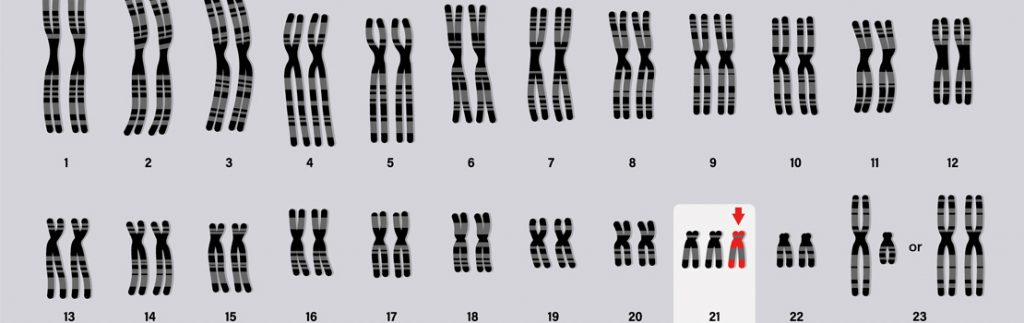
Chromosome abnormalities have profound health consequences including trisomy and cancer. Karyotyping (the visualisation of the complete set of chromosomes by shape and size) is an initial step towards identification of chromosome aberrations and disease. Other chromosome imaging methods such as fluorescent in situ hybridisation (FISH) rely on sample preparation or fluorescent markers, which may or may not alter the sample. […]
Read More… from X-ray ptychography: Seeing chromosome abnormalities in a new light
Table-top soft X-ray laser in the ‘water window’

X-rays are excellent tools for exploring the structure of matter and molecules. Professor Szymon Suckewer and his group at Princeton University, alongside Professors Olga Kocharovskaya, Marlan Scully and Alexei Sokolov of Texas A&M University, have developed a technology capable of producing X-rays, but which can fit into a standard university lab – even onto a table top. This offers new […]
Read More… from Table-top soft X-ray laser in the ‘water window’
Understanding the atomic and electronic structure of solid-density liquid carbon

How fast does a solid melt? You might think quite slowly, on a timescale of minutes to hours. However, recent experiments by Dr Emiliano Principi and his team at the FERMI free electron laser show that the melting of carbon by a laser pulse is actually an ultrafast, nonthermal process – taking less than a billionth of a second. By […]
Read More… from Understanding the atomic and electronic structure of solid-density liquid carbon
RadiaBeam: Safer X-ray sources with smaller particle accelerators

Many important technologies rely on the production of high-energy radiation, yet without the right precautions, the radioactive sources involved in these processes can be incredibly dangerous. Dr Sergey Kutsaev, together with a team at RadiaBeam Technologies, has now shown how these sources could be replaced by compact, low-cost, and flexible particle accelerators, capable of producing high-energy X-rays on demand. His […]
Read More… from RadiaBeam: Safer X-ray sources with smaller particle accelerators
Using physics to explore virus self-assembly
Through decades of research, biologists have determined that under the right conditions, viruses can assemble themselves from their constituent proteins. So far, however, many of the precise characteristics of this process have eluded researchers. Dr Guillaume Tresset at Université Paris-Saclay aims to fill these gaps in our knowledge through experiments that measure how x-rays are scattered by self-assembling viruses. His […]
Read More… from Using physics to explore virus self-assembly