Tag: university of minnesota
Labour force projections: Egypt anticipates a resumption of demographic pressures

Egyptian youths born into the ‘echo generation’ of 2006–2014 are not yet of working age, but when they do enter the labour market there will be a vast increase in the supply of workers. Professor Ragui Assaad, of the Humphrey School of Public Affairs at the University of Minnesota in the US, has been estimating the effects of this increase. […]
Read More… from Labour force projections: Egypt anticipates a resumption of demographic pressures
Could a serpin antibody help to treat type 1 diabetes?

Research from Dr Jan Czyzyk and his team at the University of Minnesota, USA, explores the balance between proteases and serpins, and how their activity can in turn affect the inflammation and tissue regeneration of pancreatic islet cells. Their findings show that antibodies can be used to change this serpin–protease balance, with interesting impacts. Excitingly, their research opens the possibility […]
Read More… from Could a serpin antibody help to treat type 1 diabetes?
Deeper insights into cell death and survival
The intricate balance between cell death and survival is essential for normal development and for preventing diseases such as cancer and autoimmunity. Ronald Jemmerson at the University of Minnesota contributed to the seminal discovery that cytochrome c (Cyt c) plays a key role in the onset of apoptosis (programmed cell death). His laboratory also established that leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein-1 (LRG1) binds […]
Read More… from Deeper insights into cell death and survival
The intricate world of the centrosome
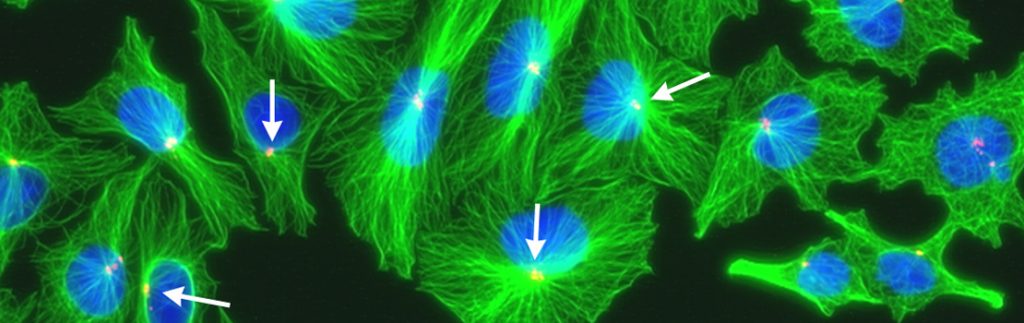
Dr Ryoko Kuriyama is a Professor at the University of Minnesota, Twin Cities. Alongside Dr Cody Fisher, she studies mammalian centrosomes, composite organelles responsible for the segregation of chromosomes during mammalian somatic cell division. Together, Kuriyama and Fisher, with the help of the United States National Science Foundation, investigate the detailed complexity of centrosome maturation, identifying the pericentriolar material protein […]
Human Leukocyte Antigens: The missing link in Alzheimer’s disease etiology

Alzheimer’s disease is a huge socioeconomic burden in developed countries. Recently, viral infections such as the herpes virus have been implicated in Alzheimer’s disease risk. However, it is unclear what the link between the two is. Professor Lisa M. James of the University of Minnesota, in collaboration with Dr Apostolos Georgopoulos and Dr Spyros Charonis, has utilised computational biology to […]
Read More… from Human Leukocyte Antigens: The missing link in Alzheimer’s disease etiology
Configuring new bonds between first-row transition metals

Transition metals are some of the most important elements in the Periodic Table for their wealth of applications, spanning catalysis to biology. The rich chemistry of the transition metals arises from their remarkable ability to form multiple chemical bonds, a process that is still not fully understood and remains a major challenge in fundamental chemistry. Professor Connie Lu at the […]
Read More… from Configuring new bonds between first-row transition metals
Open-source bioinformatic solutions for ‘Big Data’ analysis

Drs Tim Griffin and Pratik Jagtap along with the Galaxy-P team from the University of Minnesota are working to develop workflows on an open source platform for the analysis of multi-omic data. They are currently focusing on using a Galaxy-based framework to investigate the integration of genomic datasets with mass spectrometry-based ‘omics’ data. But in the long term, they aim […]
Read More… from Open-source bioinformatic solutions for ‘Big Data’ analysis
Synthetic cells have senses too
What defines a living cell? How to capture the molecular essence of life? These fundamental questions underpin the collaborative research programme led by Prof Allen Liu at the University of Michigan and Prof Vincent Noireaux at the University of Minnesota. The pair uses molecular components to construct prototypes of synthetic cells displaying the minimal characteristics of life. Their ‘cell analogs’ […]