Tag: microbes
Nivolumab against lung cancer: How is the gut–lung axis involved?
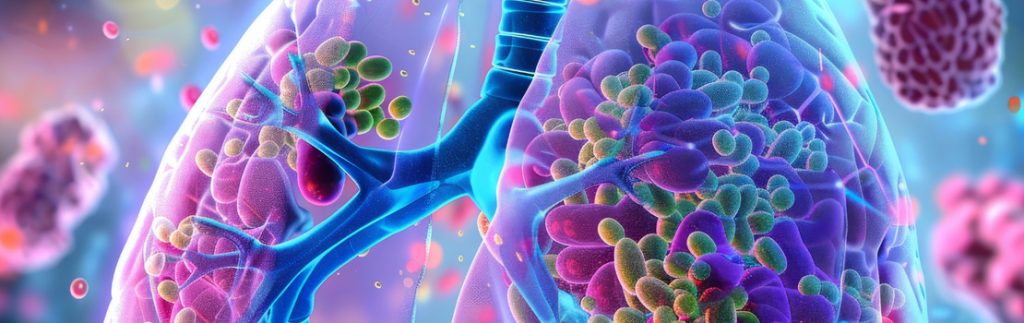
The study of the gut microbiome, which is the total of all the microbes living in the intestines, has been shown to not only play an important role in the health of the bowel itself, but also in the health of distant organs such as the lungs. Lung cancer is one of the diseases that is often difficult to treat […]
Read More… from Nivolumab against lung cancer: How is the gut–lung axis involved?
Vignette on a vital vitamin for vegans

Vitamins are organic (carbon- and hydrogen-based) molecules that are essential nutrients for humans. There are 13 different vitamins, of which the B vitamin group has eight, and they all function as co-factors (non-protein components) for various cellular enzymes. Vitamin B12 is a unique molecule that is not made in animals or plants, but it is vital for cell metabolism and […]
Controlling Salmonella in the poultry gut: Diversity is key

When microorganisms that interact in a specific environment suppress the growth of pathogens, researchers call this ‘pathogen exclusion’. Salmonella is found in poultry intestines and can harm both the birds and humans. To control Salmonella growth, a balance between microorganisms that colonise the poultry gut is necessary. This involves complex interactions between microbes that we don’t yet fully understand. Dr Margie […]
Read More… from Controlling Salmonella in the poultry gut: Diversity is key
Exploring the transfer of antibiotic resistance genes within poultry litter
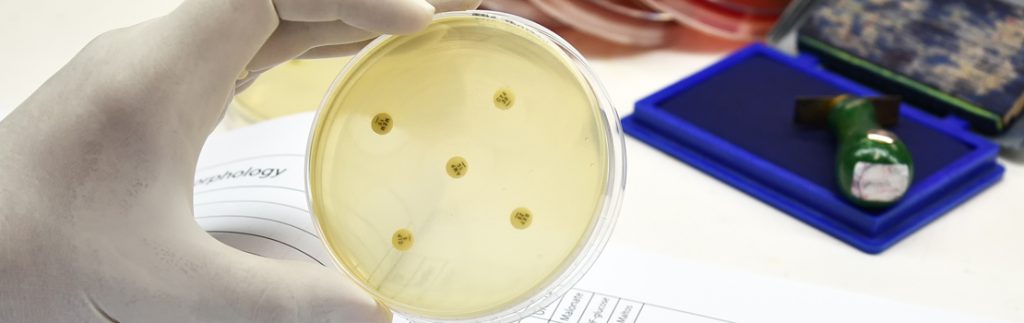
Antibiotic resistance is a major threat to human and animal health. Bacteria containing antibiotic resistance genes are found in poultry litter, usually from commercial chicken production. Since poultry litter is often used as a soil fertiliser, there is a risk that this antibiotic resistance could be transferred into the soil. Professor John Maurer at Virginia Tech University, USA, has shown […]
Read More… from Exploring the transfer of antibiotic resistance genes within poultry litter
Do bees farm microbes? Rethinking what it is to be a bee

Bees have not been eating what we thought they were. The work of Dr Prarthana Dharampal and Dr Shawn Steffan, University of Wisconsin, USA, shows bees are not strict vegetarians requiring just pollen and nectar for food. Larval bee health is also reliant on eating the microbes that are feeding on the pollen supplies. The bee larvae are further up […]
Read More… from Do bees farm microbes? Rethinking what it is to be a bee
The biodegrading functions of microbial communities in polluted freshwaters

Pollution is a selective pressure that enriches microorganisms at polluted freshwater sites. Some microbial species can adapt to the levels of pollution in water streams, displaying metabolic capacities that allow them to degrade the contaminants. Dr Ayixon Sánchez-Reyes and Dr Luz Bretón-Deval, from the Institute of Biotechnology of the National Autonomous University of Mexico, study the microbial biodiversity landscapes of […]
Read More… from The biodegrading functions of microbial communities in polluted freshwaters
Nutrient management strategies for sustainable mulberry plantations

Mulberry is a very important, economically multipurpose tree. One of its key uses is as a food source for mulberry silkworms that feast exclusively on its leaves. Therefore, finding ways to boost leaf yields/quality and growth of mulberry trees is of great interest to the silk production industry. Dr Songmei Shi and Professor Xinhua He, from Southwest University, China, have […]
Read More… from Nutrient management strategies for sustainable mulberry plantations
The ultimate veg patch: Can phytotechnology save cultivated peatlands?

Intact, water-logged peatlands are a stable store of the world’s carbon, but if drained they can become near perfect (organic) soils for growing high-cost vegetables. It was thought that you couldn’t cultivate a peatland without ruining it and releasing its carbon into the atmosphere. Dr Jacynthe Dessureault-Rompré, with her team at Laval University in Québec, Canada, has been investigating whether […]
Read More… from The ultimate veg patch: Can phytotechnology save cultivated peatlands?
Leaf spots on the prairies

Plants face a large number of threats from their surroundings. When microbes such as fungi act as pathogens on plants, they can cause disease. Some fungal pathogens of wheat appear as symptoms of spots on the leaves. Two important fungal species are the tan spot pathogen and the septoria nodorum blotch pathogen. These fungi can infect the same plant and […]
Rice husk biochar with beneficial microbes: A promising agricultural inoculant and soil ameliorant

The research of Shohei Ebe and Takashi Ano from Kindai University into the relationship between a microbe and rice husk biochar (RHB) suggests the latter is an activator of beneficial microbes that can be used to combat phytopathogenic microorganisms. Having isolated a novel lipopeptide producing Bacillus sp. that benefits from RHB presence in the soil, these are promising insights into […]